What is TACACS+ / RADIUS Access Management? How Does It Work?
Jul 03, 2022
/
Kron
Playing a central role in the business world as a result of the development of digital technologies, remote access systems have many advantages such as making workflows sustainable, increasing efficiency, and optimizing costs. However, it should be also noted that this access management model creates some difficulties in terms of cybersecurity. The key to minimizing these problems, or even not getting affected as often is to use the TACACS+ / RADIUS Access Management module.
Remote authentication allows you to store user names and passwords on your IT network in one place, on a central server. The TACACS+ protocol and the RADIUS protocol also offer a unique infrastructure for configuring relevant user names and passwords. You can configure changes on each separate network device using both protocols when a user is added or deleted, or when a user changes a password.
Moreover, let's say you only make one change to the configuration on the server. Without the need to interfere with other components in the system, the devices continue to access the server for authentication. Although the most well-known function of TACACS+ and RADIUS is authentication, it should be noted that the authorization and accounting functions are also quite effective.
What is TACACS+ / RADIUS Access Management?
Terminal Access Controller Access-Control System Plus (TACACS+) and Remote Access Dial In User Service (RADIUS) are two common security protocols to access IT networks. TACACS+ is used for administrative access to network devices such as routers and switches or devices in the network. RADIUS, on the other hand, is for authenticating and logging remote network users wanting to access your IT network. Both security protocols provide Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) management for devices connecting to and using an IT network. Exploring in detail the features of AAA management, which consists of three main components, might be useful to understand the TACACS+ / RADIUS Access Management module.
- Authentication: This feature is about who is authorized to access the network. TACACS+ and RADIUS can provide privileged accounts with a user name and password to validate their identity.
- Authorization: The second feature defines which services the user can access through network access. Thanks to the authorization policy existing in both security protocols, visitors only have access to the online environment on the network and internet, while only your IT team is authorized to access the entire password database.
- Accounting: The third feature makes it possible to keep track of what services each user access and for how long. Accounting records include the identity, network address, point of attachment, and unique session identifier of a user accessing your organization's IT network. This data is then tracked with the activity tracking method and added to the user's record. This feature can be very useful for your organization when billing and charging users or departments for the time spent in the system and the transactions performed.
Now that we've elaborated on the definitions of TACACS+ and RADIUS and their three basic features in detail, we can focus on the working principles of these protocols.
How TACACS+ / RADIUS Access Management Works?
Providing AAA management consisting of Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting stages, TACACS+ / RADIUS Access Management is a process with 9 steps and categorized under Authentication and Administration. Network Admin, Network Specialist, Backbone Specialist take an active role in this 9-step working process. In addition Active Directory (AD) helps the access management to run smoothly by ensuring that the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) phase is completed in the final phase of the process. Now, let's examine the working principle with 9 steps.
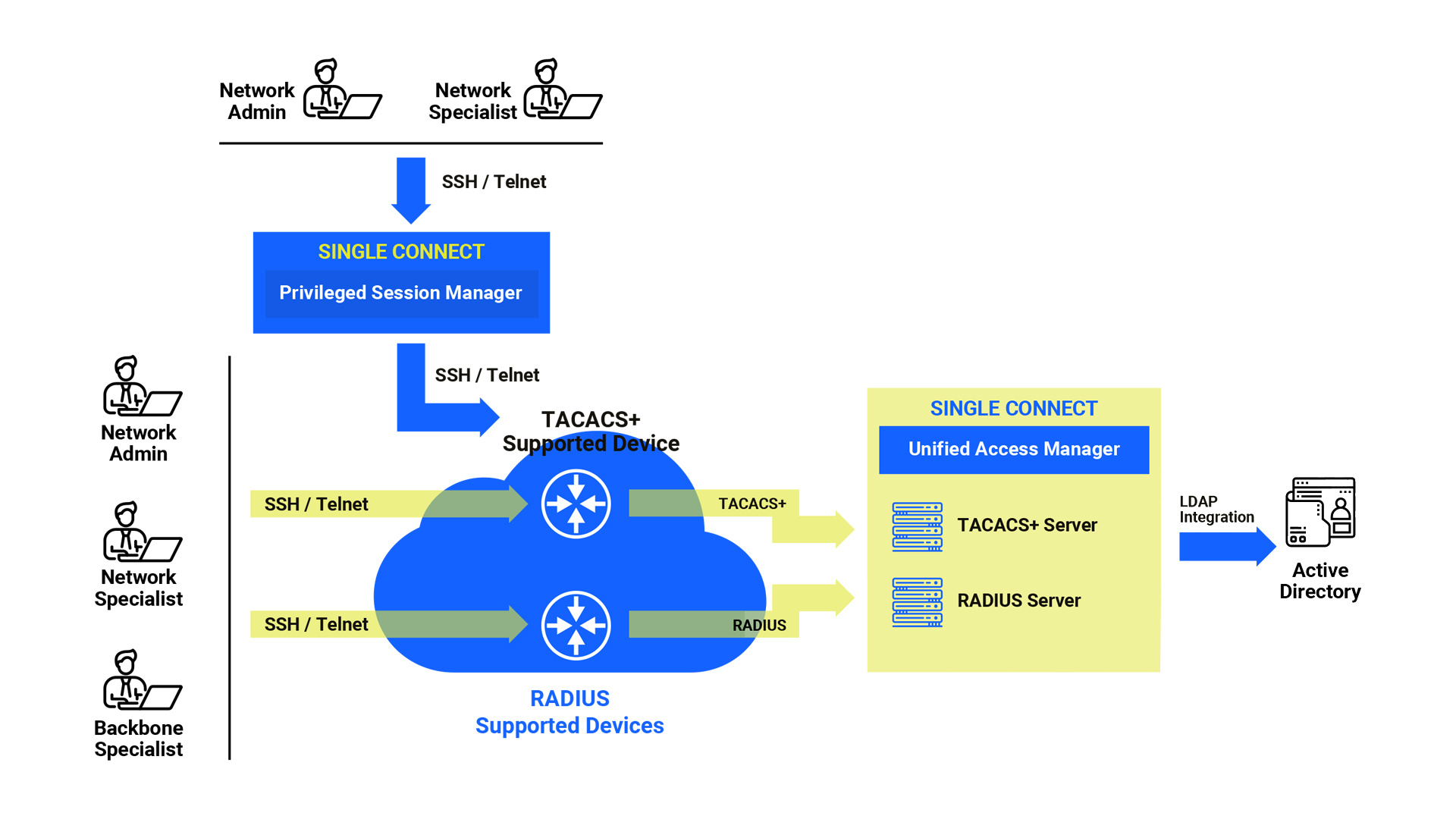
Authentication
- 1st step: The user initiates a CLI session to the target device. After then, the user enters a user name and password.
- 2nd step: The target device sends the user name and password to the TACACS+ access manager.
- 3rd step: If the user name and password are correct, a successful response is generated.
- 4th step: The target device sends the response to the user.
- 5th step: A CLI session is established between the user and the target device. After this step, the user can enter commands for device management purposes.
Administration
- 6th step: The user enters a command on the CLI screen and this command is sent to the target device.
- 7th step: The target device sends the relevant command to the access manager of the TACACS+ module.
- 8th step: TACACS+ Access Manager checks if the relevant user has the privilege to run this command. After checking, it either accepts or rejects. Logs this command with the response.
- 9th step: If the TACACS+ Access Manager responds with an accept message, the target device runs the command and sends the response to the user. If the response is a reject message, the target device sends a fail message to the user.
What are the benefits of TACACS+ / RADIUS Access Management?
TACACS+ / RADIUS Access Management has many different benefits, especially logging and multi-factor authentication. In other words, this access management model offers many more benefits under one roof than firewalls, filters, and LDAP can offer alone. For example, let's say you control an IP address with a firewall and filter. In this method, the restriction is not applied to individual clients but to devices. If you enable the IP address you control to access a particular web server, anyone at the machine with that IP address can access this server. However, when you use TACACS+ or RADIUS, all users who want to access the server from a machine with that IP address must enter a user name and password.
On the other hand, you can use LDAP to obtain directory information such as e-mail addresses and public keys. But if you need more than captive portal authentication, you should implement the 802.1X security protocol. LDAP, on the other hand, cannot easily implement this protocol because 802.1X was developed with RADIUS in mind. Challenge and response protocols such as 802.1X and MSCHAPv2 work well with RADIUS.
We can summarize the main benefits of the TACACS+ / RADIUS Access Management module as follows:
- With the standalone AAA solution, no additional platform is required to replace aging Cisco ACS servers.
- Full visibility with detailed audit logs
- Separation of duties and the principle of least privilege
- Full compliance with international regulations such as GDPR and ISO27001 with Active Directory group policies extended to the network infrastructure
- Direct access control to the target devices
- Multi-factor authentication
- Get rid of weak and/or expired passwords
- Define time-based access restrictions
- Limited privileges to each corporate department isolated from the network
- Simplifying management with Active Directory (AD) user names and passwords
- Automatically lock user account when the term of employment is terminated
- Supporting open protocol-based network devices
- Supporting Attribute Value Pair configuration
- Support 250,000 devices in a single instance
TACACS+ / RADIUS Access Management module stands out as the best Cisco ACS alternative. This module can easily replace ACS, which Cisco will stop supporting on August 31, 2022, and can be purchased simply thanks to the modular structure of Single Connect, one of the best Privileged Access Management solutions internationally.
You can contact our team for more information about our TACACS+ / RADIUS Access Management solution and Privileged Access Management (PAM) product family Single Connect.
Highlights
Other Blogs

Securing Application Credentials with Kron PAM: A Shield Against Cyber Breaches

Did Zero Trust Kill Defense in Depth or Has Defense in Depth Improved Zero Trust?